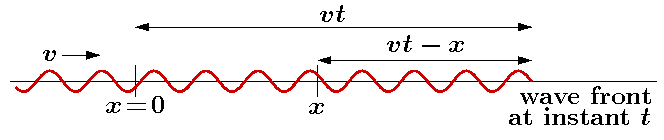
Each cycle contributes 2π
to the phase of the oscillatory movement.
Hence, the phase of the oscillatory movement
at the position x
at the instant t
is given by
phase = 2π × (number of cycles) = 2π(vt-x)/λ
Using, furthermore the definition
k=2π/λ,
we come to the conclusion that the phase of the oscillatory movement
at the position x
at the instant t
is given by
phase = k(vt-x)
|
|