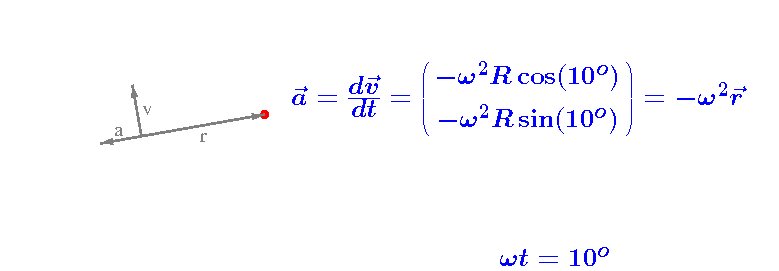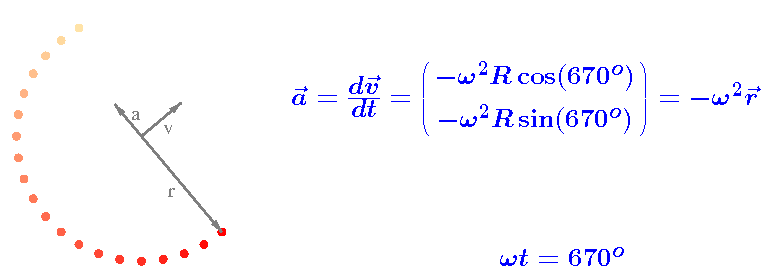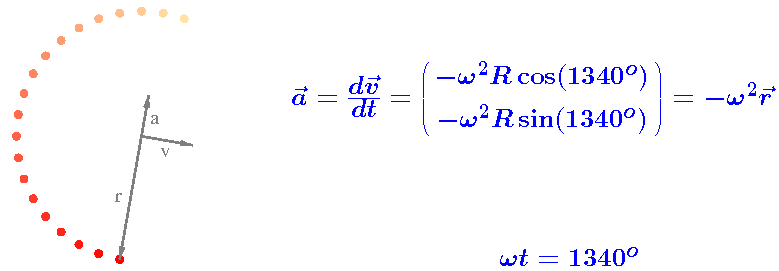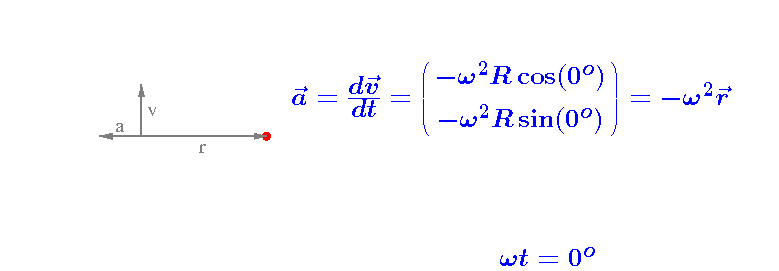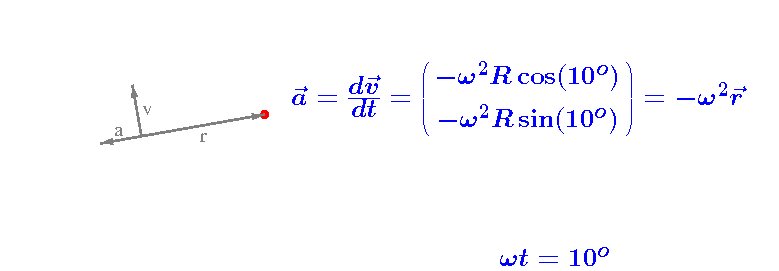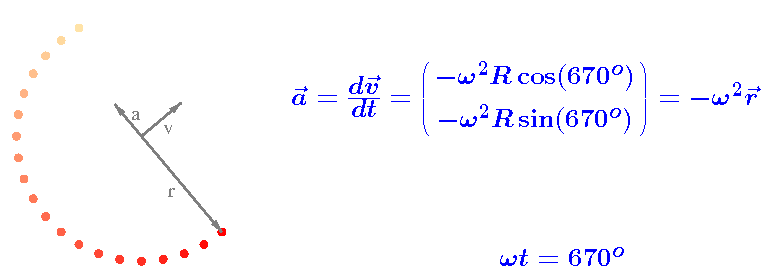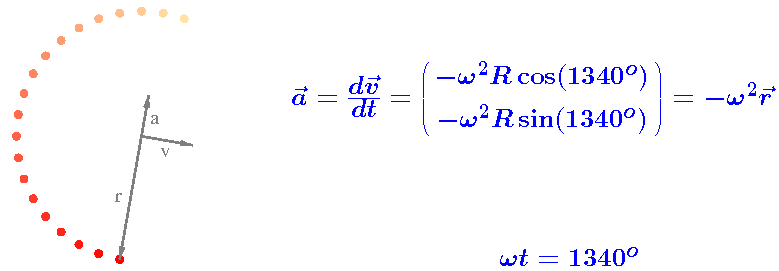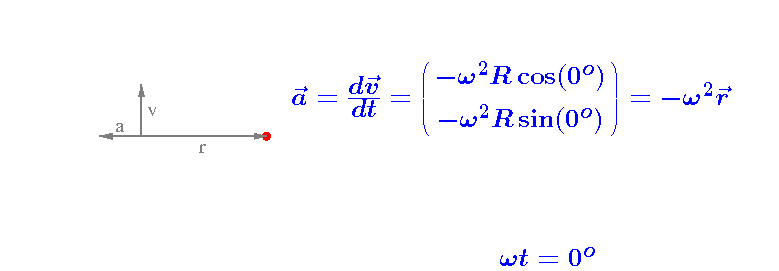The acceleration vector a
is at each instant of time t given by
the time derivative of the velocity vector
v.
|
a(t) =
dv(t)/dt =
|
(
|
|
)
|
=
|
(
|
|
-ω2R cos(ωt)
|
|
-ω2R sin(ωt)
|
|
)
|
since
dvx(t)/dt
= d( -ωR sin(ωt) )/dt
= -ω2R cos(ωt)
and
dvy(t)/dt
= d( ωR cos(ωt) )/dt
= -ω2R sin(ωt)
The resulting acceleration vector is indicated in the above video.
Notice that a and v
are perpendicular and, consequently,
that a and r
are parallel.
|
|